Atomic Radius
The atomic radius is a measure of the size of an atom. The atomic radius is defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms that are bonded together.
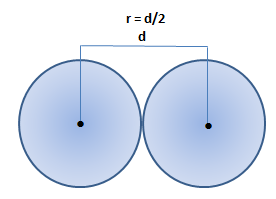 r is atomic radius of an atom and d is distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms
r is atomic radius of an atom and d is distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms
Atomic radius is dependent on the type of bond present. Types of bonds can be grouped as five descriptive types.
- Ionic bonds
- Covalent bonds
- Metallic bonds
- van der Waals bonds
- Hydrogen bonds
Units used to measure atomic radius:
- Angstroms (Å): This the most common unit used. Equivalent to 1.0 x 10-10 meters.
- Nanometer (nm): Equivalent to 1.0 x 10-9 meters.
- Picometer (pm): Equivalent to 1.0 x 10-12 meters.
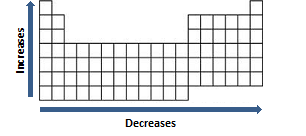
Period Trends
As you move left-to-right across a period, in general (not including the noble gases), atomic radius decreases. As you go left-to-right across a period, electrons are added to the same energy level. At the same time, protons are being added to the nucleus increasing positive charge in the nucleus. Increased positive charge in the nucleus pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
Group Trends
As you move down a group, in general, atomic radius increases. As you move down a group the number of electrons increases, thus increasesing the number of energy levels. The outermost orbital increases in size when you move down the group making the atom larger. Therefore, the atomic radius increases as the group and energy levels increase.